
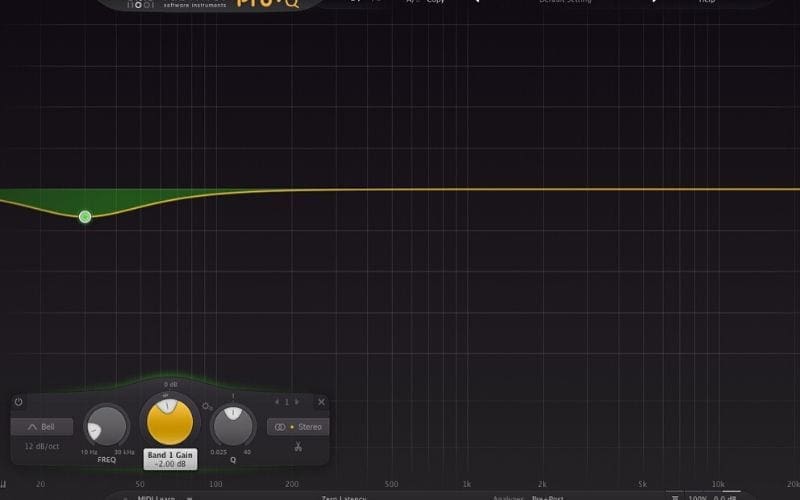
to allow you to adjust your audio settings and get the most out of your speakers. It usually works with frequencies between 20 Hz up to 20,000 Hz, which are theoretically the frequencies humans can hear, although in reality our range could be decreased by age and other factors.ĭecades ago, equalizers were managed via a physical console were you could tune up and down levers to adjust your settings, but since most audio is consumed in a digital way nowadays, equalizers have been implemented in most devices such as computers, smartphones, etc. What’s an Equalizer (EQ)?Īn equalizer is a processor that allows you to boost or decrease certain frequency ranges to modify or enhance the sound quality. Parametrics are found on sound mixing consoles and some amplifier units (guitar amps, small PA amps, etc).But first of all, let’s go over the basics as you will need to know this information to keep up with the rest of the article. Parametric equalizers use bell equalization, usually with knobs for different frequencies, but have the significant advantage of being able to select which frequency is being adjusted.
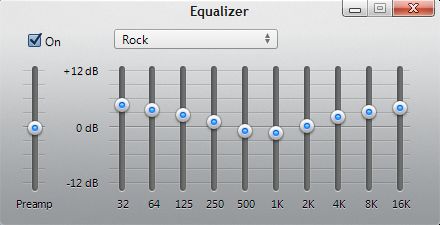
Each slider adjusts one frequency band so the more sliders you have, the more control. Graphic equalizers provide a very intuitive way to work - separate slider controls for different frequencies are laid out in a way which represents the frequency spectrum. The specified point is affected the most, frequencies further from the point are affected less. Bell EQīell equalization boosts or attenuates a range of frequencies centred around a certain point. This creates a "shelf" in the frequency spectrum. In shelving equalization, all frequencies above or below a certain point are boosted or attenuated the same amount. There are several common types of equalization, described below. Equalization can also be used for applications such as making sounds more intelligible and reducing feedback. For example, if a sound was recorded in a room which accentuates high frequencies, an equalizer can reduce those frequencies to a more normal level. The key is to be able to adjust a narrower range of frequencies without affecting neighbouring frequencies.Įqualization is most commonly used to correct signals which sound unnatural. This is adequate for very rudimentary adjustments - it only provides two controls for the entire frequency spectrum, so each control adjusts a fairly wide range of frequencies.Īdvanced equalization systems provide a fine level of frequency control. The treble control adjusts high frequencies, the bass control adjusts low frequencies. The most basic type of equalization familiar to most people is the treble/bass control on home audio equipment. Equalization, or EQ for short, means boosting or reducing (attenuating) the levels of different frequencies in a signal.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
